High healthcare expenses significantly influence individuals’ ability to access necessary medical services, shaping health outcomes across the United States. Despite most adults carrying health insurance and reporting good or excellent health, many still face financial barriers that hinder their pursuit of care. This persistent issue underscores the importance of understanding how costs affect access, especially among vulnerable populations, and highlights ongoing disparities rooted in insurance coverage, health status, and socioeconomic factors.
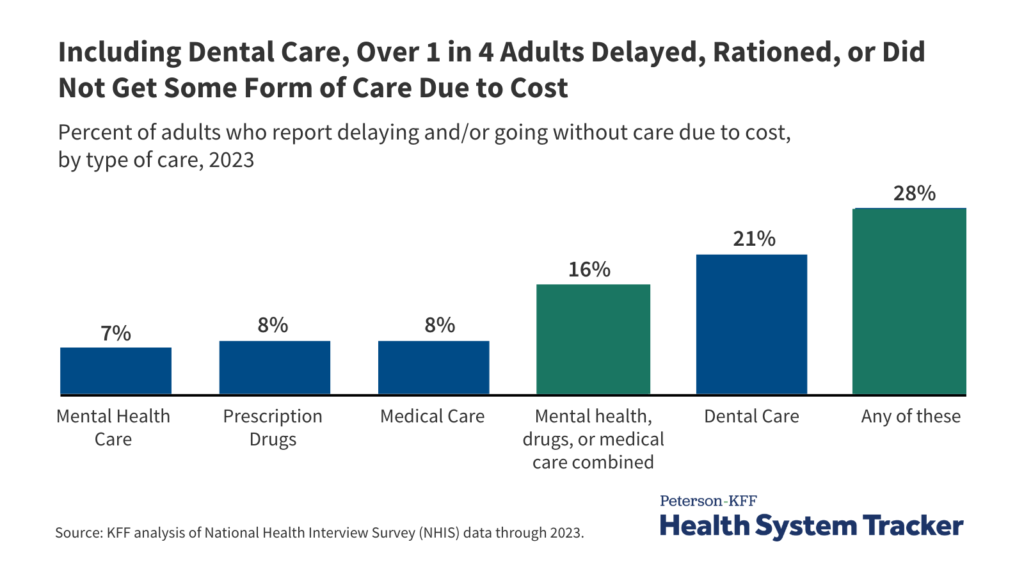
The relationship between healthcare affordability and access is complex. While a large portion of adults (92%) are insured, a substantial number report delaying or avoiding care due to costs. The 2023 data from the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) reveals that over 28% of adults have postponed or skipped some form of healthcare—be it medical, mental health, dental, or prescription medication—because of financial constraints. These barriers are particularly pronounced among uninsured individuals, those in poorer health, and racial and ethnic minorities such as Black and Hispanic populations.
Many Americans worry about unexpected medical bills, with 45% expressing concern about their ability to pay bills if faced with illness or accidents. Such worries are especially acute among uninsured adults, where nearly three-quarters (74%) report anxiety over medical expenses. This financial stress can lead to deferred treatment, worsening health conditions, and increased long-term costs for both individuals and the healthcare system.
Financial barriers extend beyond insurance status. For example, nearly 45% of adults report concerns about paying medical bills if they become ill, and a significant share—about 11%—say they or a family member have difficulty settling medical debts. These issues disproportionately affect Black Americans and those in worse health, who are twice as likely to face payment difficulties compared to their healthier or white counterparts. Such disparities highlight the critical need for policies that address both coverage gaps and the affordability of care.
Access issues are also reflected in the availability of routine healthcare services. Uninsured adults are nearly five times more likely than insured individuals to lack a usual source of care, which hampers preventive health efforts and early intervention. Additionally, adults with incomes below 200% of the federal poverty level are almost twice as likely to forgo care due to cost, emphasizing how socioeconomic status heavily influences healthcare utilization.
Interesting:
- How does ai reduce costs in healthcare
- How mobile devices are revolutionizing healthcare operations and patient care
- The growing crisis of healthcare costs and medical debt in the united states
- Understanding hipaa its impact on healthcare and privacy protections
- How smartphones are transforming healthcare key benefits and challenges
The rising costs of medications, especially insulin, have also been a concern. In 2021, about 17% of insulin users reported rationing their doses or delaying purchases due to high prices. Recent legislative measures, such as those introduced in the Inflation Reduction Act, aim to reduce medication costs for Medicare beneficiaries, including a cap on insulin prices, thereby easing some financial burdens.
Despite ongoing reforms, many barriers remain. Insurance problems—such as unexpected out-of-pocket costs, denials of coverage, or complicated prior authorization processes—continue to impede access. A 2023 survey found that over 28% of insured adults experienced delays or problems related to their health insurance that affected their care. These issues contribute to delays, unmet needs, and sometimes even declines in health status, illustrating that having insurance alone does not guarantee affordable or accessible healthcare.
The role of emerging technologies, like artificial intelligence in healthcare pharmaceuticals and sports, offers promising avenues to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Similarly, innovations such as VR and AR in healthcare are transforming patient engagement and medical training, potentially lowering expenses and enhancing access. As the healthcare landscape evolves, integrating these advances could help mitigate some financial barriers and promote more equitable health outcomes.
Understanding the full scope of how costs influence healthcare access requires recognizing the multifaceted nature of barriers—financial, structural, and technological. Efforts to improve affordability, expand coverage, and leverage innovative solutions are essential to ensuring that all individuals can receive timely and necessary care without the threat of financial hardship. Policymakers, providers, and technologists must work together to address these challenges, fostering a more equitable and accessible healthcare system for everyone.
For additional insights on developing user-centered healthcare solutions, see guidelines for creating effective healthcare applications. As technological advancements continue to reshape medicine, understanding the intersection of innovation and affordability remains crucial for improving access and health outcomes nationwide.