The integration of augmented reality (AR) into healthcare is transforming medical procedures, training, and patient engagement at an unprecedented pace. As technological advancements accelerate, the market is projected to expand significantly, driven by innovations in hardware, software, and application areas across the globe. This report explores the current market landscape, key trends, growth drivers, challenges, and competitive dynamics shaping the future of AR in healthcare through 2030.
Market Overview and Growth Drivers
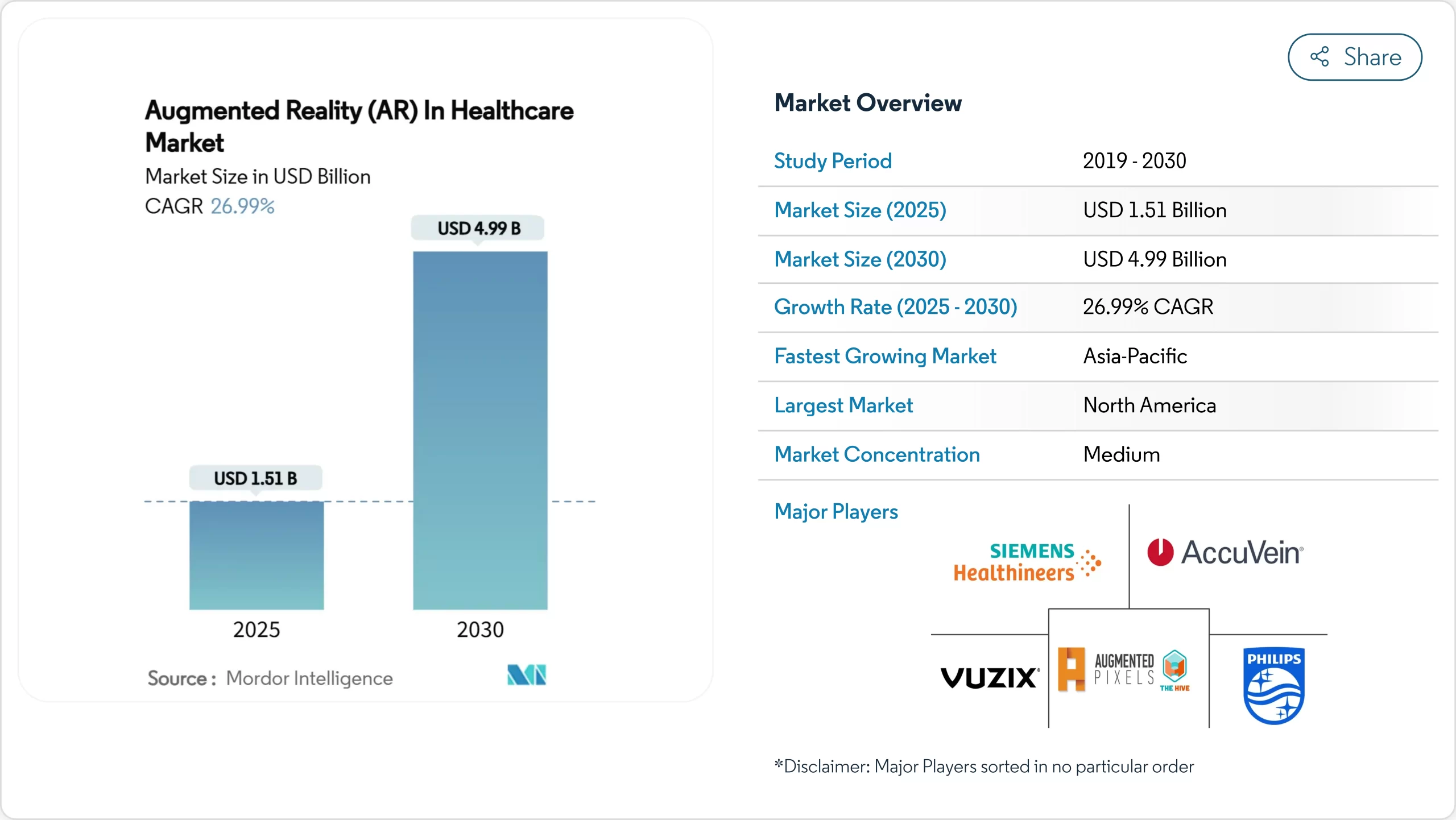
The augmented reality sector within healthcare is valued at approximately USD 1.51 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach nearly USD 5 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of nearly 27%. This rapid expansion indicates a shift where hospitals, training institutions, and home care providers are transitioning from isolated pilot projects to integrated, enterprise-wide systems. These systems enhance surgical precision, reduce learning curves for medical professionals, and increase patient participation in their own care. The increasing number of FDA clearances for intra-operative AR devices and the pandemic-driven emphasis on touchless visualization tools have made AR a standard clinical requirement rather than an experimental technology.
Adoption is strongest in North America due to its mature reimbursement infrastructure, while Asia-Pacific is experiencing the fastest growth owing to government-funded initiatives aimed at addressing physician shortages. Competitive pressure is intensifying as major device manufacturers embed AR into imaging systems and startups conduct multi-center trials to validate efficacy, further fueling market expansion.
Key Market Segments and Trends
Component Breakdown
In 2024, hardware still accounted for the majority of revenue, holding about 55.45%, but services are quickly catching up, projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 28.54% through 2030. The shift towards comprehensive service contracts that include workflow integration, data security, and outcomes monitoring reflects a broader trend of moving from hardware sales to ongoing support and software solutions.
Technological Advancements
Handheld devices such as tablets and smartphones contributed around 38.54% of revenue in 2024, thanks to their familiarity and ease of use. However, head-mounted displays are rapidly gaining popularity, with a CAGR of nearly 29%, due to their hands-free capabilities vital for complex surgical procedures. The development of lightweight, high-resolution headsets with gesture control and sterilizable components is pushing AR towards mainstream clinical adoption.
Application Focus
Surgical planning and guidance remain the dominant application, representing over 42% of revenue in 2024. The ability to overlay detailed anatomical visuals in real-time enhances precision and safety during surgeries. Medical training, patient education, and rehabilitation are also expanding areas, significantly improving outcomes and patient understanding.
End User and Geography
Hospitals and clinics are the primary revenue generators, with research laboratories experiencing the fastest growth—almost 30% annually—due to ongoing experimental and validation efforts. Geographically, North America leads in market share, but Asia-Pacific is projected to outpace other regions with a CAGR of approximately 28%, driven by government initiatives and increasing healthcare investments.
Trends and Insights
Advancements in Surgical Training
Immersive AR simulators are revolutionizing surgical education by reducing errors and shortening training durations. Major centers report lower complication rates when residents utilize AR modules beforehand. Voice-controlled navigation and real-time anatomy manipulation lower infection risks and improve efficiency, aligning with outcomes-based reimbursement policies. As cloud-based libraries grow, the pace of training and credentialing is expected to accelerate further.
Rising Investment in AR Startups
Venture capital pouring into AR healthcare startups is accelerating product development and deployment. Companies like Augmedics have secured hundreds of millions of dollars in funding, supporting widespread adoption of AR-guided surgical systems. Strategic acquisitions by giants such as Stryker and Philips are fueling integration and market penetration, emphasizing the importance of clinical data and interoperability.
Interesting:
- The future of healthcare growth and innovation in augmented and virtual reality technologies by 2030
- The future of healthcare growth and innovation in augmented and virtual reality technologies
- The growing crisis of healthcare costs and medical debt in the united states
- The transformative power of mobile healthcare and ai in shaping patient care by 2025
- The influence of hipaa on modern telemedicine and healthcare privacy standards
Demand for Minimally Invasive Procedures
AR-assisted minimally invasive surgeries are demonstrating significant clinical benefits, including reduced blood loss and fewer postoperative complications. Overlays that visualize hidden vessels and critical structures enable surgeons to perform more precise, tissue-sparing interventions. Financially, hospitals are experiencing shorter stays and lower readmission rates, contributing to favorable economic outcomes.
Enhancing Patient Engagement and Rehabilitation
AR tools are increasingly used to educate patients by visualizing their anatomy and procedural steps, reducing anxiety and improving consent quality. Post-stroke rehabilitation programs employing AR and gesture-tracking technologies are boosting recovery rates and adherence. As 5G networks expand, remote AR-based therapy and cross-border tele-rehabilitation will become more prevalent, especially in underserved regions.
Challenges and Restraints
High Initial Investment
The cost of AR hardware, which can start at USD 5,000 for basic glasses and exceed USD 250,000 for comprehensive surgical suites, remains a significant barrier, particularly for smaller institutions. Limited reimbursement codes and interoperability challenges further hinder widespread adoption. Leasing options and evidence of process efficiency gains are helping to mitigate these costs, but funding constraints persist.
Data Privacy and Cybersecurity
The integration of live imaging, electronic health records, and biometric data into AR systems increases the attack surface for cyber threats. Regulatory frameworks such as HIPAA and GDPR impose stringent requirements, demanding robust encryption and multi-factor authentication. Hospitals and vendors are investing heavily in cybersecurity measures, although these add to system complexity and deployment time.
Regulatory and Validation Hurdles
The lack of standardized regulatory pathways and long-term clinical validation remains a concern. Many AR solutions are still in experimental stages, and hospitals require proof of safety, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness before full-scale adoption. These factors slow down market growth, particularly in emerging markets.
Market Dynamics and Competitive Landscape
The AR in healthcare market is characterized by a moderately fragmented landscape. Major players like Microsoft, Siemens Healthineers, and Philips leverage their extensive device ecosystems and regulatory expertise, while startups such as Augmedics and Surgical Theater focus on specialized surgical niches. The industry is shifting from hardware innovation to workflow integration, with a growing emphasis on software, cloud services, and cybersecurity.
Mergers and acquisitions are increasingly driven by the desire to acquire clinical data, interoperability standards, and AI capabilities. Companies that succeed in embedding AR deeply into clinical workflows and establishing strong support services will dominate long-term.
Future Outlook
The market’s trajectory suggests continued growth driven by technological innovation, regulatory acceptance, and expanding clinical applications. Emerging regions like Asia-Pacific will be significant contributors, supported by government initiatives and increasing healthcare infrastructure. The integration of AR with other digital health tools, including telehealth and health informatics, will further accelerate adoption.
For more information on how to differentiate between basic life support and CPR, visit here. Additionally, understanding the nuances between various certifications can be crucial for healthcare providers; learn more at this link. As AR continues to reshape healthcare security policies, organizations should also consider enhancing their protective measures. The role of health informatics in safeguarding patient data is vital, emphasizing the importance of securing health information systems.